Liquid ethylene is the liquefied version of ethylene, a flammable gas that is increasingly used across a number of industries.
The simplest alkene, its worldwide demand has grown from 152 million metric tons in 2017 to a forecasted 185 million metric tons in 2022, according to figures published in Statista. This expanding demand responds to the growth of ethylene uses in sectors such as the chemical and the petrochemical industry.
Keep reading to find out what exactly liquid ethylene is and how companies can store it in a safe and efficient manner.
Different uses of liquid ethylene
Ethylene uses are varied and involve a number of industries:
- The petrochemical industry uses ethylene to produce multiple products, including polyethylene, ethylene dichloride, glycols, ethanol and styrene, among others. In fact, polyethylene is perhaps the best known of ethylene uses, consisting of polymer chains.
- It’s a key part of LNG liquefaction plants, as it plays a role in refrigerating this substance. The growing importance of LNG thus is causing a boost in the demand for ethylene.
- It plays an important role in the chemical sector, as it’s used as the source and intermediate substance for several syntheses.
- The agricultural sector uses ethylene to produce plant hormones, facilitate plant growth and control the ripening of certain fruits and vegetables.
- The automotive sector uses ethylene to manufacture car glasses.
- Ethylene is used in the medical sector as an anaesthetic.
- The metallurgical sector also makes use of liquid ethylene in a number of processes, including welding and metal cutting.
Liquid ethylene on the industries
Liquid ethylene is obtained when ethylene is refrigerated and pressurized by applying low or cryogenic temperatures. This is done in order to facilitate the transportation and storage of this element, and mainly demanded by industries that need easy access to it.
A number of industries present a particular interest in storing and using liquid ethylene, including refineries, petrochemical plants, fertilizer plants and nuclear and power plants.
Ethylene Glycol
Ethylene glycol is a chemical compound derived from ethylene that presents distinct uses:
- It’s employed to generate antifreeze formulations which are useful in deicing aircrafts, among other services.
- It plays a crucial role in manufacturing polymers, such as PET or polyethylene.
- Ethylene glycol is also needed as a dehydrating agent for LNG, as this substance is saturated with water vapour when removed from its underground sources.
- It’s employed in a number of manufacturing processes, including the making of ink, explosives or fiberglass.
You may like: Discover the latest advances in cryogenic technology
Storing liquid ethylene
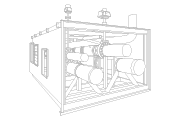
In order to guarantee that liquid ethylene preserves all its properties, it must be stored at low or cryogenic temperatures. Thus, ethylene storage presents particular challenges and the need for special ethylene tanks which are typically custom-made for low temperatures.
Challenges of storing ethylene
- Vaporizers must be installed in order to prevent heat loss and pressure loss when this element is removed from ethylene tanks. This is done in order to avoid any safety risks derived from pressure losses and eliminate the potential downtime needed to bring the ethylene tanks back to their normal state.
- Insulation and refrigeration systems might be needed in order to maintain cryogenic temperatures.
- The safety measures in ethylene storage stations include installing them on well-ventilated places that are free from any moisture sources; and protecting them from electricity, physical damage, sources of ignition and oxidizing substances. Outdoor storage is preferred.
Ways to store liquid ethylene
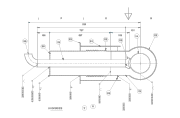
- Liquid ethylene can be stored on vertical and horizontal tanks. The first option is the most economical but requires a bigger space.
- Ethylene tanks can range from 5 tons up to 200 tons in terms of capacity.
- They must incorporate all safety measures, including valves, unloading pumps, and safety fittings;
- They’re made from stainless steel (inner tank) and carbon steel (outer tank). The space between these two layers provides the necessary vacuum to guarantee the thermal insulation, while other insulating materials can be incorporated.
- Additionally, ethylene tanks will typically be flat-bottom structures.
- From the ethylene storage facilities, liquid ethylene will then be transported to liquefaction plants using ad hoc transportation systems.
Keep reading: Cryogenic systems and how they’re revolutionizing almost every industry
All in all, companies must ensure the design for their ethylene storage is in the hands of experienced and up-to-date engineering teams that can guarantee an optimal and safe ethylene tanks’ design and implementation.
The process will involve a series of steps: from the design phase through advanced technology and software tools; the supply of the necessary materials; to the analysis of the best possible system for each project’s needs. At the same time, this engineering project will need to adapt to local, national and international regulations, while also applying recognized standards.
If you want to contact an expert team in the storage and transport of liquid ethylene and other substances, Cryospain is the answer. We have carried out numerous custom installations for gases such as ethylene, even in large flat-bottomed tanks. Take a look!



 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns