An understanding of the importance of a particular cryoline and its characteristics allows us to choose the most suitable type of cryogenic pipe for each type of project. It is furthermore essential that we know how to choose each model in the correct size for each installation line, as this will be key in its performance over time.
Why is it important to choose the correct cryogenic pipe size?
Errors in the size of a cryoline are a common problem in this type of installation and this will often end up affecting its performance.
One of the situations in which it is especially critical to choose the correct size of this type of pipes is when there is a low flow versus a high flow in the cryogenic pipes in the system. There is often a tendency to think that a larger pipe size offers a margin of safety, but if the flow of the system and the time it takes to cool are not taken into account, this can often prove not to be the case.

Problems arising from choosing the wrong cryogenic pipeline
Cryogenic liquids require very low temperatures to remain in their liquid state, as when they begin to heat above boiling point they create vapour in the cryogenic line or system tank.
If the liquid is even allowed to stand at room temperature, it will turn into vapour, which will need space to escape, regardless of whether the unit is operating or not. The use of vacuum-jacketed piping reduces the heat input, increasing the time window before vaporisation, but it must be understood that the process will still happen.
Another common problem even in vacuum insulated cryogenic piping is the naturally occurring heat leakage, either because the larger diameter pipe allows the liquid to receive more heat, or because there is a point in the low flow systems where the heat input evaporates the cryogenic liquid.
Finally, it should also be noted that when a cryogenic pipe is not used for a long period of time, the cryogenic liquid can heat up and turn into a gas, which in turn heats up the pipe. The pipeline must therefore be cooled again to prevent the liquid from changing phase, because until this happens, the liquid will not be pure again.
Factors that should be considered when determining the correct sizing for cryogenic pipe
Before deciding on the correct size for a cryogenic pipe, the following factors must be considered to ensure the right calculations can be made:
- The required system flow, which is determined by the amount of liquid needed at the end points of the system, as well as the duty cycle of the equipment, which in some cases demands a long time to turn off and on when in use.
- System pressure, which may vary depending on the supply tank, according to its type, the condition it’s in, the connections used and the cryogenic liquid supplier.
- Minimum and maximum pressure requirements of the end-use equipment to enable it to function properly.
- System restriction points, such as in-line filters or elbows, which may affect the amount of liquid reaching the end point.
Related content: Why you should choose vacuum insulated pipes
What are the main types of cryogenic pipes?
When we talk about cryogenic pipelines, we must have a grasp of the characteristics and uses that distinguish each one. We normally refer to the following types:
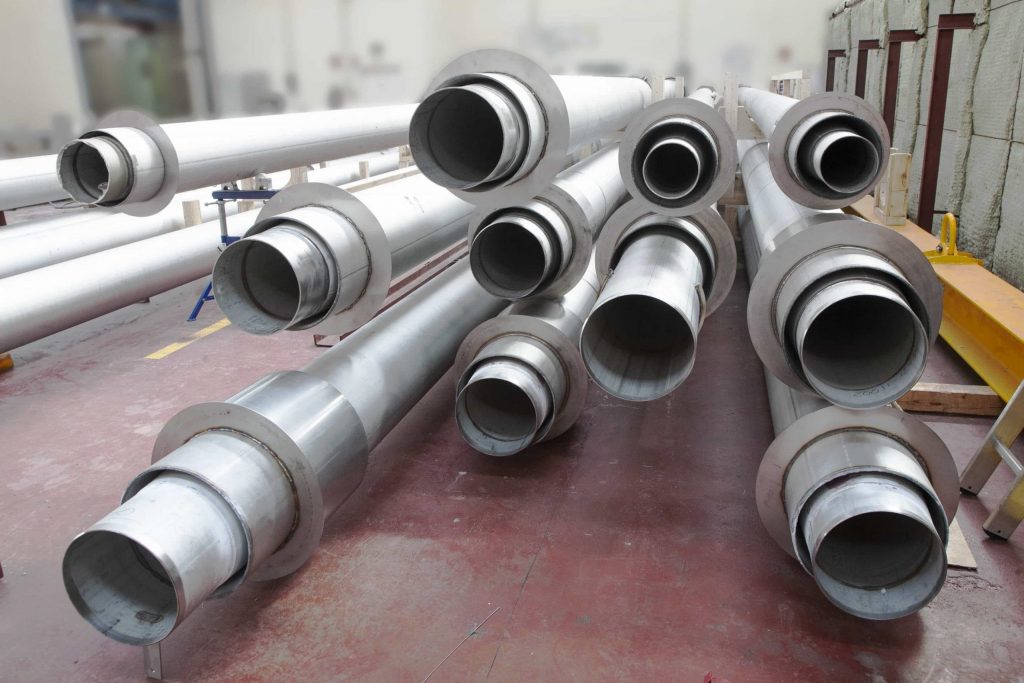
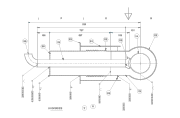
1.Vacuum insulated rigid transfer pipes (VIP), which are the basis of most cryogenic infrastructures. They are supplied in the form of prefabricated sections, which cannot be articulated. Therefore, their dimensions must be precisely calculated in advance to ensure that they are manufactured accurately to allow them to fit perfectly into the designed system.
These elements consist of an inner and an outer tube. The space between the two is sucked out through a valve, while spacers are used to ensure that they do not touch each other. In addition, compensators are fitted to absorb the material stresses due to the upper cooling of the inner part. Stability and quality are thereby guaranteed at a very low cost.
It is worth noting that this type of piping is used for the safe transport of cold liquid gases, without them suffering excessive heating that would cause them to change state and, therefore, reduce their quality.
2. Vacuum insulated flexible transfer lines. These elements have a slightly lower insulation value than the previous ones, but are designed for projects requiring greater flexibility. These pipes are suitable when regular coupling and uncoupling is required in, for example, a service station.
These pipes are also advantageous when connected to transfer lines with applications in which they will be mobile or undergo vibrations, as well as on ships or transport vehicles. It should also be noted that they are the most suitable option in cases where the pipes cannot be accurately measured prior to installation.
To sum up, taking into account the different types of cryogenic piping that exist and the best system for measuring their dimensions is an indispensable step if we want to get the most out of the installation of these elements in a cryogenic system.




 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns