Vacuum jacketed piping plays an essential role in providing efficient piping for cryogenic liquids in industrial plants.
What exactly is vacuum jacketed tubing and how does this type of vacuum insulated pipe installation work in order to avoid heat losses and other inefficiencies? Keep reading to find out.
What is vacuum jacketed piping?
Vacuum jacketed piping is a type of tube equipment ideal for transferring liquid cryogen substances necessary for different types of industrial plants, whether indoors or outdoors.
Also known as vacuum insulated piping, VJ piping and vacuum jacketed tubing, it’s used to transfer cryogenic gasses in liquid form, including liquid oxygen, liquid nitrogen, liquid helium and other types of technical gasses.
Through a specific design, these installations are able to avoid heat transfer processes and heat leaks and thus they keep substances at the desired cryogenic temperatures.
While vacuum jacketed piping has been available since the early 1990s, current developments have allowed this technology to provide better insulation and an easier installation and maintenance.
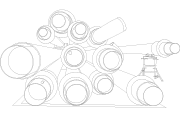
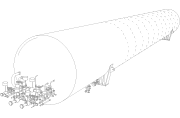
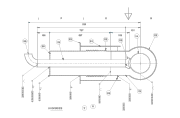
Generally speaking, a vacuum jacketed pipe consists of a system made of an inner and an outer pipe. Wrapped in super-insulating materials, the inner pipe is in charge of carrying cryogenic liquids. A vacuum is created between the two pipes, protecting liquids from undesired heat losses.
However, each vacuum jacketed piping may take a different design approach, so that each cryogenic substance’s specific requirements are met.
Through vacuum jacketed tubing, industrial plants are able to efficiently transfer cryogenic substances, guaranteeing no additional costs or issues arise. The right vacuum jacketed piping system provides the following benefits:
- Heat leaks that affect the quality and performance of cryogenic substances, turning them inconsistent are avoided. Vacuum jacketed tubing thus preserves the quality of substances, guaranteeing they’re kept cold and liquid.
- Evaporation problems are eliminated. Heat leaks result in gas losses that leave the system, while proper insulation guarantees minimizing them and, as a consequence, remaining efficient and minimizing costs.
- They reduce excessive vapor issues and hindered cooling capacities
- Eliminate the emergence of ice, which can appear if gas losses build up, leaving pipes when they’re still at very cold temperatures.
- Hygiene issues such as moisture on pipes and other applications can also be avoided. A vacuum jacketed piping system is easier to be cleaned, preventing bacterial growth and facilitating easier maintenance processes. This is key in certain industries, such as the medical and pharmaceutical sectors. Regulated by strict standards and norms, the use of vacuum jacketed tubing facilitates guaranteeing hygiene and eliminates potential bacterial contaminations.
- Because vacuum insulated piping minimizes gas leaks, their financial consequences and potential safety risks are also reduced. The system thus becomes a safe alternative to guarantee employees and systems’ safety.
- These systems are easy to maintain. Produced and transported to the building site in separate sections, they’re then connected and assembled in a supervised process.
Types of vacuum jacketed pipes: what are they made of?
There are two types of vacuum jacketed piping:
- Rigid systems include two rigid pipes. They’re generally easier to install and typically present 10-year periods where no deterioration can be observed and no maintenance is needed. During the installation process for rigid vacuum jacketed piping, pipe sections are assembled using bayonet fittings to guarantee great vacuum-insulated, frost-free links.
- Flexible or bendable vacuum jacketed pipes consist of a system of two convoluted pipes (inner and outer) that are also installed using bayonet connectors. This type of vacuum jacketed piping is usually more economical, providing significant cost-savings in their productions.
This is due to these structures’ flexibility, which avoids more costly layout measurements. Additionally, because of their flexibility, it’s also possible to employ these systems in different locations in case there’s a change of plans or if they’re used to optimize an already existing system. Their transportation to the construction site is also less expensive, as they can be fitted in multiple transport options, including air freight and more economical road options.
When it comes to materials for vacuum jacketed piping, these are chosen for their capacities to prevent heat transfer processes and heat loss. For this reason, stainless-steel is typically the main material employed in a vacuum jacketed pipe system.
Additionally, a number of materials are used to provide proper insulation and avoid conduction, radiation and convection heat transfer issues. These typically include:
- Radiant heat barrier materials
- Non-conductive spacer materials
You may like: Pipe in Pipe: the ideal cryogenic pipes for bunkering plants
Uses of vacuum jacketed piping
Vacuum jacketed piping plays a key role in a number of sectors as a crucial part in industrial plants in need for transferring cryogenic substances such as LIN (liquid nitrogen), LOX (liquid oxygen), LAR (liquid argon), LNG (Liquefied Natural Gas), LHe (Liquid Helium), LH2 (Liquid hydrogen).
In fact, the growing demand for vacuum jacketed tubing is a testament of how cryogenic substances are revolutionizing almost every industry.
The following are some of the most common applications:
- As the importance of liquid oxygen (LOX) in the medicinal and pharmaceutical industry grows, both industries are in need of vacuum jacketed piping that adjusts to their requirements.
The metallurgy industry is also increasingly adopting LOX for a number of processes
- While the applications of liquid nitrogen expand through a number of sectors (such as freezing and transporting food, cryopreservation of biological samples, refrigeration for superconductors, and cryotherapy treatments for skin), a vacuum jacketed pipe system can be the right solution for efficiently transferring this substance.
Liquid nitrogen is also increasingly important for the aerospace and aeronautical sector, as companies develop solutions that use it as a greener fuel alternative.
- Liquid argon plays a key role in welding and other processes part of the siderurgy sector. It’s additionally employed in creating protective atmospheres, degasification and desulphurization.
- The growing importance of liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) in industries such as the automotive sector is turning vacuum jacketed piping into a much demanded installation for this industry. It’s also key for other industries such as the metallurgical, food, textile and ceramic sectors.
As the shipping industry moves forward cleaner energy alternatives, vacuum jacketed piping is used for bunkering and retrofit projects.
- The use of liquid helium is growing in relevance in sectors such as aeronautics and aerospace, scuba diving, electronics manufacturing, hospitals, welding and steel manufacturing and transportation equipment.
- Liquid hydrogen remains a key substance for the energetic industry, transportation, food industry, aerospace and refineries.
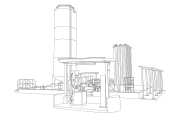
Industrial plants where vacuum jacketed piping is needed
Considering the cryogenic substances mentioned above and their current uses today, the following are some of the industrial plants where vacuum jacketed piping can typically be found:
- Metallurgical facilities
- Medicinal and pharmaceutical industries
- Air Separation Units and plants
- Transportation tubes for LNG in bunkering and ship retrofit projects
- Industrial and manufacturing plants, including the food sector and electronics, among other products
Keep reading: Cryogenic pipes: tips for choosing the right line size
Our experience with vacuum jacketed pipes
Cryospain is in charge of designing and manufacturing vacuum jacketed pipes according to the most strict international regulations.
Additionally, our two decades of experience in the field of cryogenic engineering allow us to provide our clients with tailor-made cryogenic equipment that aligns to their specific requirements in terms of installation and space inside the industrial plant.
Get in touch with us and speak to our technical team to learn how we can help you achieve the right vacuum jacketed piping system for you.





 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns