Liquefied natural gas is projected to play a central role in the global energy landscape in the coming decades. Driven by its major advantages, being the cleanest fossil fuel, abundant, and highly compatible with renewable energy sources, LNG is reshaping energy markets by providing reliable supply during peak demand.
Below, you’ll find a clear explanation of what LNG is, the main uses of liquefied natural gas, and the best types of LNG tanks for safe and efficient storage.
What is LNG?
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas that has been cooled to a liquid state to simplify storage and long-distance transportation.
When natural gas reaches approximately –260°F (–162°C) through a liquefaction process using cryogenic heat exchangers, its volume becomes 600 times smaller than in its gaseous state. This dramatic reduction is one of LNG’s main advantages, making global transport viable without pipelines.
Although liquefaction technology was developed in the 19th century, modern applications and rising global demand have turned LNG into a strategic energy resource. For example, U.S. exports of LNG increased by 42% (2.8 Bcf/d) during the first half of 2021 compared with the same period in 2020, according to the U.S. Department of Energy’s LNG Monthly.
Key advantages of liquefied natural gas
- Extensive global reserves, offering strong supply capacity compared to other fossil fuels.
- Efficient distribution and storage, making it possible to respond quickly to shifting energy demand.
- Cleaner combustion than other fossil fuels, providing a lower-emission alternative for industry and transportation
Main uses of liquefied natural gas
The primary application of LNG is as a reliable energy supply, particularly in scenarios where demand fluctuates or infrastructure is limited.
Key LNG use cases:
- Domestic heating: LNG supports household energy demand, especially during consumption peaks.
- Industrial applications: Industries use LNG to power processes involved in manufacturing electronics, textiles, pharmaceuticals, plastics and more.
- Transportation: The mobility sector is increasingly evaluating LNG as a cleaner alternative to traditional petroleum-based fuels.
Related content: Cryogenic plants: how we design and create tailor-made units for our clients
Storing liquefied natural gas (LNG)
LNG is a clear, non-corrosive liquid made of at least 85% methane and weighing less than water. Because it is stored at cryogenic temperatures, specific technologies and tank configurations are required to maintain safety and stability.
Different LNG storage containers and their characteristics
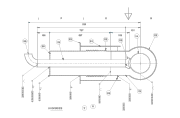
Safe LNG storage requires cryogenic tanks designed to maintain extremely low temperatures and prevent product loss.
These storage systems typically include:
- Above-ground, low-pressure tanks (below 10 kilopascals).
- Double-wall structures with a vacuum layer that provides thermal insulation.
- Mechanisms to remove small quantities of heat that enter the system over time.
- Typical LNG tank capacities range from 1,000 to 30,000 m³:
- Larger tanks are generally cylindrical with a domed roof.
- Smaller tanks may use horizontal or vertical pressure vessels, with operating pressures ranging from less than 50 kPa up to more than 1,700 kPa (7.3–246.6 psi).
In modern designs, additional safety measures often include:
- High-nickel steel inner walls
- Outer concrete containment
Keep reading: LNG Bunkering Stations for shipping, Explained
Cryospain’s role in LNG storage solutions
Cryospain provides specialized engineering expertise for the design and construction of flat-bottom cryogenic tanks used in LNG storage systems.
Our LNG storage tanks feature:
- Double-wall steel structures
- High-performance insulation such as cellular glass, expanded perlite, or rockwool
All equipment is developed according to leading international quality and safety standards, including:
- Mechanical and seismic design: API620, API650, ASME, EN14620, EN14015, EUROCODE
- External access: EN ISO14122-1/3, OSHA 1910.23/24
- Additional regulations: EIGA/CGA/127/13/E, NFPA 59A
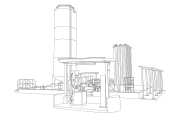
A LNG success story: Santa Cruz de la Sierra (Bolivia)
One of Cryospain’s latest milestones took place in Santa Cruz de la Sierra, Bolivia, where we supplied and deployed a flat-bottom cryogenic tank for LNG storage as part of a “virtual pipeline.” This solution enables the distribution of natural gas in remote regions where pipeline installation is not feasible.
The project presented several challenges:
- A remote location deep in the jungle and high in the mountains
- Limited local access to qualified personnel
- Harsh environmental conditions such as constant heat and rainfall
- Complex logistics involving the shipment of more than 25 containers from Spain
- Double customs processes in Chile and Bolivia
- Difficult overland transport due to rugged terrain
Despite these obstacles, the project was completed successfully, allowing thousands of residents to transition from heavy hydrocarbons (fuel oil, diesel) to cleaner natural gas, benefiting both the community and the environment.
If you want to learn more about our engineering capabilities or discuss how we can support your next cryogenic project, get in touch with our team, we’re ready to help you.





 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns