As more and more industries continue discovering the potential of cryogenics to enhance and extend their possibilities, the cryogenic vessel has become an essential part of many operations.
Because cryogenic substances require maintaining extremely low temperatures, there are certain requirements that need to be met by the storage tanks meant to hold liquid nitrogen, liquid oxygen or liquid argon, among other substances, under the right conditions.
From our experience in facilitating cryogenic equipment for companies, at Cryospain we want to share some tips in this brief guide about cryogenic tanks.
What is a cryogenic vessel and what types exist
A cryogenic vessel is a recipient designed to maintain the right conditions for cryogenic substances to thrive. This means cryogenic tanks must present thermal isolation systems and be able to withstand abrupt temperature and pressure changes.
The use of the cryogenic vessel ensures an efficient storage and transportation of cryogenic substances, which represents an advantage in terms of storage space (as liquefied gasses occupy less space) and safety in handling these materials.
There are different types of cryogenic vessels, while a common configuration includes double-walled cylindrical tanks where inner tanks are made of stainless steel and outer tanks made of carbon steel, filled with an insulation material. High-vacuum configurations are put in place to minimize heat losses.
The choice will depend on the specific fluid it contains and the required size and storage capacity. Some of the common shapes for a cryogenic vessel include:
- Laboratory jars
- Rangers
- Dewars
- Cryogenic vessels
- Cryogenic tanks
- Flat-bottom cryogenic tanks
- Cryogenic cisterns for trucks
- ISO containers for cryogenics
- Pressurized cryogenic storage tanks
Pressure vessels
Pressure vessels are containers designed to hold substances at pressure values different from ambient pressure. In order to do so, and to guarantee safety, certain parameters must be taken into account, including maximum design temperatures, corrosion allowance and safe operating pressure and temperature values.
Related content: Insulated vessels, the technology that adapts to your needs
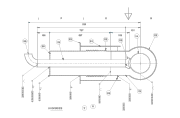
Main components of a cryogenic vessel
For a cryogenic vessel to be able to hold these substances, it must adapt to the specific environmental characteristics it will encounter, including size, location, weather and types of soil, among other conditions.
The liquid kept inside (nitrogen, oxygen, argon, liquefied natural gas, liquified petrol gas, ethylene…) will also greatly condition the features of the cryogenic vessel.
However, and although customization plays a key role in developing the right cryogenic vessel, it’s possible to generally speak of the following three components for these storage tanks:
Inner vessel
This part is in direct contact with the cryogenic fluid and contains it, so that it’s typically made of stainless steel able to withstand very low temperatures without cracks or other issues.
Outer vessel
Also known as the vacuum jacket, this part is made of carbon steel and is in charge of guaranteeing insulation, acting as a protective wall avoiding heat transfers from the outside environment.
Insulation system
With large scale cryogenic tanks, both vessels are divided with a vacuum space to guarantee insulation. Other options are available, including the addition of a combination of insulation materials.
Pressure regulation system
Additionally, tanks are typically provided with a system in charge of regulating pressure, which is specifically designed to make pressure remain constant and match the needs of each user.
Particularities and safety considerations when working with a cryogenic vessel
In order to guarantee a safe and efficient installation of cryogenic vessels and their supplementary components, as well as the rest of the elements, the next considerations must be taken into account:
- Choosing the right location. This applies to both outdoors and indoors equipment. As a general rule, it’s wise to locate the cryogenic vessel close to where the cryogenic substance is being use.
- Foreseeing potential safety risks. This involves putting together the right enclosing system, in order to avoid leaks, as well as evacuation routes within the premises and the avoidance of bituminous products
- Considering vehicle accessibility. A key consideration is how will the cryogenic substances be replenished.
- ITC-MIE.AP10 standards, as expressed in rules regarding pressure devices, must be followed and complied with.
Read more: Vacuum Insulated Vessels – New Large-Scale Cryogenic Storage
Cryospain, designing custom cryogenic vessels for each industry
Cryospain is in charge of designing, producing, installing and maintaining cryogenic vessels, including the following types: flat-bottom cryogenic tanks, pressurized cryogenic storage tanks and cryogenic tanks.
We’re able to implement turnkey projects for cryogenic vessels and tailor-made equipment, basing our work in our team of engineers and technicians and their experience, as well as two fully-functional production centers.
Our more than two decades of experience in cryogenic engineering guarantee we’re also able to provide maintenance help in multiple cryogenic vessel configurations, including laboratory jars, rangers and dewars, cryogenic vessels, tanks, flat-bottom tanks, cryogenic cisterns for trucks, ISO cryogenic containers and pressurized cryogenic storage tanks.
Find out more about our services and how we can help you access the cryogenic vessel you need: get in touch with us and speak to our team today.




 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns