Ducting pipes are an important asset for a number of modern industries: from allowing modern construction methods to industrial uses and more. We take a deep, their common uses and look at the crucial role of cryogenic ducting pipe.
What is a ducting pipe?
A ducting pipe, pipe duct or duct tube is a conduct that delivers or removes substances or energy, acting as a passage or channel.
Used to deliver cables, heat and/or cold, as well as gaseous substances, thus play a key role in a number of fields and productive sectors.
Applications of a ducting pipe
Some common uses include:
- Heating, ventilation and air conditioning ducting pipes are in charge of guaranteeing thermal comfort and air quality in modern constructions
- Underground ducting systems work to protect cables and utility pipes in buildings, including those transporting water, gas and other substances. They help protect inner pipes from being damaged (for instance, can help dispersing gas leaks, avoiding water leaks or water contamination, among other potential issues).
- Welding operations make use of flexible ducting pipes to guarantee fume extraction
- The food industry uses them to transport ingredients in production lines
Different types of ducting pipes
According to color
Ducting pipes present different colors in order to help operators, construction workers and anyone who has access to them to identify what type of utility passes through the pipe. Although it varies from region to region, the most common color code is:
- Orange: cables for traffic signals and street lighting
- Black: low-voltage electricity cable on a domestic context
- Yellow: service and gas pipe
- Purple: cables for highway communication
- Blue: water pipes
According to material
- PVC duct pipe and UPV pipes: they are common for domestic appliances
- Round metal duct pipe, such as pipes made from galvanized steel, are common in air duct systems
- Polyethylene (PE): a popular choice for solid wall pipes
- Twinwall HDPE ducting pipes are preferred for cases where additional protection is necessary, such as underground installations
Rigid or flexible pipes
A flexible ducting pipe comes in coils (spiral ducts) and can be bent in different angles. They’re typically made in polyurethane (PU) and PVC and can present additional insulation layers for thermal and acoustic comfort.
On the other hand, rigid ducting refers to a ducting pipe that is inelastic and can’t be bent easily.
Different classes for electric cables
In the case of ducting pipes for the transmission of electricity, there are three classes:
- Class 1 is for high-voltage installations
- Class 2 for low voltage
- Class 3 for general applications
You must be interested: Cryogenic pipes: tips for choosing the right line size
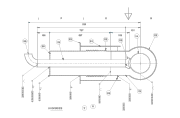
Cryogenic ducting pipes
A cryogenic ducting pipe is an insulated duct pipe that is manufactured so that it is able to withstand extremely cold temperatures.
There are several views on what constitutes a cryogenic duct tube: while some regard them as the systems that are able to withstand -290C temperatures (representing the point from which carbon steel materials start presenting embrittlement); some others believe cryogenic piping systems are those that operate below -1500C (-3000F).
Cryogenic pipes play a key role in the transportation and industrial processing of liquefied technical gases such as nitrogen, oxygen, butane, methane, liquefied natural gas (LNG), ethylene, or ammonia, among others.
In order to provide effective insulation, cryogenic piping present certain design requirements that help guarantee the transportation and storage of such substances is efficient and safe:
- The choice of materials must be guided by cryogenic engineering expertise, as this type of pipe will experience corrosion and other types of deterioration. Common materials for cryogenic ducting pipes include stainless steel, aluminum alloy, copper alloy and copper nickel alloy. Additionally, other non-metallic materials are used for different components in cryogenic ducting pipe, including mineral wool, fiberglass, polyurethane, styrofoam, grafoil, or reinforced Teflon, among others.
- Suitable insulation technologies must be put to work in order to avoid heat losses or heat gains by environmental causes, which would make the system inefficient and potentially dangerous. The insulation might result in increased weight and rigidity in cryogenic piping systems.
In order to guarantee the necessary insulation, there are a number of technical possibilities that can be looked into, which include the use of expanded foams (such as polyurethane or foam glass); the use of perlite in powder insulation systems; employing vacuum insulation; or techniques based on evacuated powder and fibrous insulation, among other potential solutions.
- Appropriate support and valve systems must be installed in order to withstand the amount of gases that are generated when cryogenic substances are vaporized. On the contrary, sealed containers would present safety issues due to pressure build-ups.
- Cryogenic pipe systems must also take into account that the outstanding thermal stresses created when materials are subjected to extremely low temperatures mean that materials contract. In order to compensate for this effect, they must use materials that present adequate flexibility.
- At the same time, decreased temperatures can also cause materials to become brittle, which is another factor to consider in the design and production of cryogenic pipes.
- Prior to being put to work, cryogenic piping must be subjected to a number of tests in order to guarantee they will be able to withstand the conditions necessary for their efficient performance.
Want to learn more about cryogenic ducting pipes?
At Cryospain we’re experts in the design and production of super-insulated pipes for cryogenics using high-vacuum systems. Download our cryogenic piping catalogue and get in touch with our team of experts to see which piping solution matches your needs.





 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns