Refrigerated tanks or refrigerated storage facilities represent a revolution for global transportation and the possibilities to use a number of substances that require temperature control.
This includes the shipping of food, medicines and technical gases, thus becoming a key part of distribution cycles and commerce on a global scale today.
What are refrigerated tanks and what are their current uses nowadays? Keep reading to find out.
What is a refrigerated tank?
Refrigerated storage tanks or refrigerated tanks are storage options which have been used for decades to store substances that must be kept under certain temperature conditions.
These include a number of liquefied gases such as ethylene, propane, butane, LNG and ammonia, among others, which are stored under very low or cryogenic temperatures (from -45 F to -270), as well as specific atmospheric pressure conditions.
Refrigerated tanks thus minimize heat losses and help maintain specific atmospheres in order to guarantee the product within is not affected by unwanted thermal or pressure changes.
Refrigerated storage facilities are designed to incorporate specific accessories and technologies that stabilize their internal atmosphere according to each substance’s needs.
They might employ diverse refrigerant methods. For instance, a tank that uses freon as a refrigerant will also be known as a freon tank.
Additionally, there are several types of refrigerated tanks:
- Pressure vessels
- Pressure spheres, which are the preferred method to store intermediate levels of substances (neither too abundant nor too scarce)
- Vertical cylindrical tanks are the most common solution to store big quantities of refrigerated liquids.
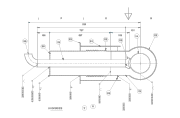
These tanks may present double-wall structures to amplify their thermal insulation capacities. If this is the case, these two concentric tanks will leave a vacuum space between them, which may also be filled with additional insulating materials.
The outer layer may include an additional insulation layer. At the same time, this type of refrigerated storage facilities may be flat-bottomed; and their roof be designed on a dome or an umbrella-shape, in case the pressure needed goes beyond atmospheric levels.
In order to guarantee the refrigerated tanks’ safety, the cryogenic tank design must take a number of things into account:
- Their filling and emptying cycles and the ways to perform them safely
- An analysis of their heating coil systems
- Industry data can be consulted in order to learn from past failures. Developing a risk-prevention plan will involve identifying failure modes and generating consequence scenarios. It’s also possible to estimate the Probability of Failure (POF) by analysing historical and current data
- A diameter of 4.5 metres is the typical limit for refrigerated tanks
- Refrigerated storage tanks will need a series of accesories to guarantee their optimal and safe performance, including a vacuum pipe, pump skids, cold boxes, valves, and safety valves.
Refrigerated tanks vs other technologies
- Heated tanks: This type of tanks are used to transport temperature-sensitive chemicals that are used in many industries, like the automotive industry, machine and construction industries. In these, the temperature is controlled using hot water,steam, glycol, electric heating systems…
- Super insulated tanks: This unit has a better insulation thickness to extend the temperature hold time and reduce the possible temperature variations of the product contained. These tanks are usually used for food that do not require refrigeration but do need to be kept cool or warm within a specific temperature.
Keep reading: Things you need to keep in mind when working with refrigerated ammonia tanks
Uses of refrigerated tanks
Refrigerated tanks are used to store liquefied gases that go from a range of boiling points from between -126.6°C a -1.1°C (-260°F a +30°F) and thus require cryogenic temperatures to be safely and efficiently stored. This includes ethylene, butane, refrigerated LPG and other substances mentioned above, for which normal, room-temperature pressure is not feasible.
Refrigerated containers
Refrigerated containers are a specific type of shipping container or intermodal container used for intermodal freight transport, which uses two or more types of transportation (typically sea, rail and road) modes in order to reach their destination.
These types of containers are used to ship products that need certain temperature control, ranging from fresh products to medical devices and chemical substances.
Some of these refrigerated containers incorporate a refrigeration unit powered externally at land-based electrical points. If needed, diesel-powered generators can also be incorporated into refrigerated containers, in order to guarantee their efficiency during transit as well.
Water-cooling systems can also be included to control temperature, while air ventilation is usually a more economical option. In fact, both systems are commonly combined in refrigerated containers.
Other options for refrigeration systems include the use of frozen carbon dioxide ice or liquid nitrogen, which are preferred for shorter trips. However, this system only works as long as the frozen gas is within the system. For railcar transport, this system has been able to provide refrigeration for more than 15 days.
At Cryospain, we’re experts in developing cryogenic storage solutions. We design, manufacture, and commission high tech cryogenic engineering installations and equipment. Contact us if you have any questions or requests.




 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns