The uses of nitrogen are expanding as progress is made in the possibilities for efficient storage and transport of this substance, at the same time as new industries are developed.
Cryospain analyses the industrial use of nitrogen in its cryogenic version in different economic sectors and the best options to guarantee that this element is stored and transported efficiently.
What is nitrogen and what types are there?
Nitrogen is an inert, odourless and colourless element whose atomic number is 7 and which is present in four-fifths of the volume of air in the atmosphere.
Because it is an inert element, it can displace oxygen. This has driven nitrogen applications in different industrial and economic sectors, which has made this substance one of the most demanded.
In this sense, nitrogen is marketed mainly in gas form and, somewhat less commonly, in liquid form.
Liquid nitrogen must be kept at cryogenic temperatures (equal to or less than -198.5ºC), which requires specific equipment. However, it is liquid nitrogen that allows greater efficiency in transport and storage.
Related reading: Cryogenic liquid gases: differences and common uses of LNG, LIN, LOX, LAR and LC02
Nitrogen uses in industry: What are gaseous and liquid nitrogen used for?
Aerospace and aeronautics
There are many different uses of nitrogen this area, since it is valued for its ability to prevent combustion processes in high pressure and temperature atmospheres, thus guaranteeing safety.
The uses of nitrogen in this area include pressurising components in industrial autoclaves and in discharge pumps.
In the aeronautical industry, it is used to inflate tyres on aircraft and to inflate rescue equipment (such as escape slides), also preventing combustion processes and explosions.
Transport
Safer, more efficient inflation and eliminating internal oxidation are also appreciated uses of nitrogen in the automotive industry.
Chemicals
There are many applications of nitrogen in the chemical industry, starting from the base that nitrogen reacts with hydrogen to obtain ammonia. Products such as fertilisers, dyes and explosives, among others, are obtained from this combination.
Nitrogen is also used for preparing liquid samples in chemical analysis, helping to create inert atmospheres.
Energy
Nitrogen is used in the energy industry with the aim of preventing gas losses, maintaining balanced pressure levels, preventing combustion and acting as an obstacle to oxygen and moisture propagation. It therefore plays an important role in oil and gas well drilling, operations and maintenance.
Food
The main uses of nitrogen in the food sector are for food conservation and safe and hygienic packaging.
It also plays an important role in the wine sector, avoiding oxidation processes, and in pressurising beer barrels.
Iron and steel
The iron and steel industry uses nitrogen in various processes. For example, it is used to produce stainless steel and to purge equipment and tanks linked to this process.
Electronics
Nitrogen is used to create controlled and inert atmospheres for manufacturing electronic products in processes such as soldering printed circuit boards and electrical and semiconductor circuits.
Health sector
Nitrogen is used to freeze biological samples of all kinds to avoid damage in transport and conservation processes. The health sector also uses liquid nitrogen for the destruction of diseased tissue.
Other
Liquid nitrogen is used in the manufacture of many other products, from light bulbs to fire-fighting tools. This element has also recently been incorporated into innovative cuisine.
How is nitrogen transported?
Nitrogen transport and storage requires two types of systems:
- High-pressure containers. They can come in various sizes and offer high-pressure environments for the correct conservation of this element.
- Pipe networks. A system for supply and transport from the storage location, especially for sectors that require high nitrogen consumption.
You might be interested in: Cryogenic liquids: what they are, how they are obtained and what they are used for
Experience with nitrogen uses
Cryospain offers the following solutions to make it easier for companies from all sectors to access the nitrogen uses mentioned above:
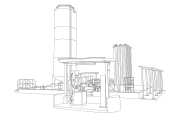
- Storage in high-pressure tanks and filling stations: Cryospain designs, supplies and installs this equipment, complying with the necessary rules and regulations and guaranteeing maximum safety and efficiency.
- Transport through Cryospain’s super-insulated high-vacuum pipes, Cryoline: designed for transporting LIN, they are an effective solution for avoiding energy losses or gasification processes.
- Flat bottom cryogenic tanks: Cryospain designs, manufactures, assembles and commissions this type of solution for storing low-pressure liquefied gases. It can therefore supply turnkey cryogenic tanks adapted to customers’ projects:
In this sense, Cryospain’s work in designing, manufacturing and installing a liquid nitrogen tank in Taiwan aimed at obtaining LIN for manufacturing microchips is distinguished as a success story.
Cryospain has therefore generated an efficient and safe system in a particularly challenging environment, with high seismic activity and extreme winds and typhoons. It also optimises transport costs and customs problems by collaborating with a local partner for manufacturing parts.
In short, Cryospain works to find the best storage and transport solution for nitrogen and other cryogenic substances for customers, adapting to their needs. Contact us to receive further details from our technical team on how we can help you.





 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns