Cryogenic liquids are gaseous substances that have been cooled to extremely low temperatures until they reach their liquid state. These fluids play a fundamental role in sectors such as industry, medicine, scientific research, aerospace, and food processing, thanks to their ability to preserve, cool, and pressurize materials with high efficiency.
In this article, you will discover what cryogenic liquids are, how they are produced, how they are classified, which are the most commonly used, how they are stored, and what risks are involved in their safe handling.
What are cryogenic liquids and how are they obtained?
Cryogenic liquids are gases that have been intensely cooled until they reach boiling points close to or below -100 °C. This cooling process must always be carried out below ambient temperature using controlled refrigeration and liquefaction systems.
Although each cryogenic gas has specific physical and chemical properties, they all share a fundamental characteristic: small amounts of liquid can rapidly expand into large volumes of extremely cold gas, making them highly efficient.
Classification of cryogenic fluids
Cryogenic fluids can be classified into three main groups based on their chemical behavior and level of risk:
Inert gases
These gases do not undergo significant chemical reactions. They are not flammable and do not support combustion.
Main examples:
- Nitrogen
- Helium
- Neon
- Argon
- Krypton
Flammable gases
The gas generated by these cryogenic liquids can ignite in the presence of air.
Most common examples:
- Hydrogen
- Methane
- Liquefied natural gas (LNG)
Don’t miss our project Flat-bottomed tank in Morocco: a step towards LNG advancement
Liquid oxygen
Cryogenic oxygen requires a separate classification due to its strong ability to intensify combustion. Materials considered non-combustible can burn violently in its presence, and organic substances can react explosively. For this reason, its handling requires specific and highly strict safety protocols.
The most commonly used cryogenic liquids in industry
Cryogenic fluids are widely used in sectors such as medicine, industrial manufacturing, transportation, aerospace, scientific research, and specialized laboratories.
Keep reading: Everything you need to know when choosing cryogenic tanks for gas storage
Liquid Hydrogen
Liquid hydrogen is one of the most widely used cryogenic liquids and has strong future potential, especially due to its role as a clean energy source and its versatility in industrial and technological applications.
To remain in a liquid state, it must be cooled and pressurized to an approximate temperature of -252.87 °C, which reduces its volume and makes storage and transport easier. Its applications span multiple industries:
- Energy: Used as a cooling gas thanks to its high thermal efficiency.
- Transportation: Works as a clean fuel for vehicles, reducing emissions while maintaining good driving range.
- Food industry: Improves food quality and safety during processing.
- Aerospace: Used as fuel for rockets and to power systems in space.
- Petrochemical: Helps convert heavy crude oil into higher-quality refined fuels.
Liquid nitrogen
Liquid nitrogen is one of the most widely used cryogenic liquids and is maintained at an approximate temperature of -196 °C. Its applications span multiple industries:
- Aerospace: manufacturing lightweight and highly resistant materials
- Automotive: welding of parts, frames, and structural components
- Medicine and biotechnology: preservation of biological samples, egg freezing, and dermatological cryotherapy
- Food and haute cuisine: rapid freezing and food preservation
- Metallurgy and industrial welding
Liquid helium
Liquid helium has the lowest boiling point of all known elements, which is why it is widely used in:
- Aerospace industry: pressurization of fluid systems on the ground and in flight
- Automotive: testing of critical components and leak detection
- Professional diving: mixed with oxygen to facilitate breathing at great depths
- Electronics industry: rapid cooling of semiconductors and circuits
- Healthcare sector: operation of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment
Other popular cryogenic liquids
Other freezing liquids widely used for industrial, medical, and food-related purposes include:
- Liquid carbon dioxide (CO₂): used in indoor cultivation to increase agricultural yields and in food processing
- Liquid oxygen: improves efficiency and productivity in industrial processes
You might be interested in: Everything you should know about storing liquefied natural gas (LNG)
How to store cryogenic liquids
Cryogenic liquids are stored as compressed gases at extremely low temperatures. If accidental decompression occurs, the gas expands rapidly, which can cause structural rupture or explosions in the containers.
For this reason, storage systems must comply with international standards for safety, design, and structural quality.
Cryogenic vessels: storage types
Cryogenic temperatures can make many conventional materials, such as plastics, rubber, or carbon steel, brittle. Therefore, specialized materials are used.
Pressure vessels for storing these fluids include:
- Large-scale industrial cryogenic tanks
- Laboratory flasks
- Large-capacity Dewar vessels
Materials for storage containers
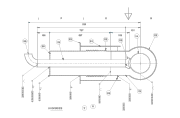
Although cryogenic vessels vary in shape and design depending on the substance they hold, industrial containers are composed of a structure divided into three fundamental parts:
- Inner vessel: made of austenitic stainless steel or aluminum, designed to withstand extreme temperatures
- Outer vessel: generally made of carbon steel, which protects the structure
- Insulation layer: composed of high-efficiency vacuum and thermal insulating materials
Large-capacity tanks also incorporate a pressure regulation system, which maintains stable and safe levels during operation.anks, and an internationally recognised design code (by country) is used to ensure that the tanks are manufactured to the millimetre.
Read more: Uses and curiosities of liquid ethylene
All designs follow international cryogenic engineering codes, ensuring structural precision and maximum safety.
Hazards when working with cryogenic fluids
Operations involving cryogenic liquids are extremely delicate. Even the smallest mistake can result in a serious accident, such as fire or explosion hazards. This is why seemingly harmless actions can trigger a disaster.
Main hazards of working with cryogenic liquids
- Rapid gas expansion (up to 700 times its original volume), which can cause explosions and asphyxiation in seconds
- Bronchial and eye freezing due to exposure to cold vapor
- First-degree burns caused by direct contact with the liquid
- Hypothermia and frostbite injuries from contact with the cold vapor emitted by these gases
In addition, direct contact with the liquid can cause first-degree burns and frostbite or hypothermia injuries. This is why it is essential to use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) for the eyes, hands, and body, and to always follow relevant safety measures, paying special attention to eye protection.
Instructions to be followed when working with cryogenic liquids
Insulated containers (Dewars) used for the transport and storage of cryogenic liquids must be handled strictly in accordance with established safety guidelines. Hermetically sealing these containers can lead to dangerous pressure buildup and significantly increase the risk of explosion due to oxygen condensation.
Always work with cryogenic fluids in open or well-ventilated areas to avoid oxygen loss and the risk of dizziness or suffocation.
Never transfer liquids in enclosed spaces. Keep an eyewash station and emergency shower nearby, and make sure the work area is clean and free of grease and flammable materials.
Cryospain: Reliable cryogenic solutions
Are you looking for a reliable technology partner that provides the most innovative and advanced cryogenic engineering solutions on the market?
Cryospain offers professional technical consulting and cutting-edge technology to help you successfully tackle your cryogenic projects.
Contact our team of experts to guide you through your next challenges and projects.





 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns