The use of renewable hydrogen stands out as a key alternative in the global effort to decarbonize energy and industry, aimed at combating climate change.
In fact, the production of hydrogen for chemical industries and refineries currently accounts for 6% of global natural gas use and 2% of coal consumption. It is also responsible for 830 megatons of CO2 emissions annually, according to the IEA.
In this context, achieving green hydrogen is crucial to minimizing the environmental impact of this element, which is also opening increasingly viable opportunities for use as a clean fuel.
What exactly is renewable hydrogen, and what role does it play today and in the future of the industry? Let’s delve into it.
What is renewable hydrogen?
Although hydrogen is an abundant element, it is found combined with other elements (such as oxygen and carbon). Its production involves separating it from these elements.
Renewable hydrogen derives its name and association with sustainability from its distinctive and environmentally friendly production process.
Unlike conventional hydrogen, renewable H2 is obtained through electrolysis, where electricity is used to separate hydrogen from the water molecules it is chemically bound to.
Keep learning: Discover the latest advances in cryogenic technology
Cuando esta electricidad proviene de fuentes de energía renovables, el resultado es energía de hidrógeno 100% renovable.
Producing renewable hydrogen
In simple terms, producing renewable hydrogen involves breaking down water molecules.
By using electrodes submerged in water (ideally powered by renewable energy), a direct current is generated. The water must also contain salts and minerals, which conduct the electricity. The process concludes when the electrodes attract ions of opposite charges, separating hydrogen and oxygen.
Differences between grey hydrogen and renewable hydrogen
Grey hydrogen is produced from natural gas. While it is currently a more cost-effective method, it is highly polluting and increasingly penalized. Producing one ton of hydrogen via this method emits up to 12 tons of CO2.
In contrast, green hydrogen follows the electrolysis process described above. While currently more expensive, its costs are expected to decrease significantly in the near future.
Industrial uses and applications of renewable hydrogen
- Energy storage: Renewable hydrogen plays a vital role as an energy carrier in storing surplus energy from renewable sources using compressed hydrogen tanks.
- Industrial production: It is used to produce ammonia, alcohols, synthetic fibers, cosmetics, glass, and steel, among other materials.

- Fuel: Hydrogen serves as a clean-burning energy source, emitting only water vapor. It is increasingly utilized in fuel cells—a technology initially developed by NASA for space missions. Fuel cells convert chemical energy into electrical energy and are becoming more efficient. Today, hydrogen-powered fuel cells are nearly twice as efficient as gasoline engines. Due to the vast potential of renewable hydrogen, companies worldwide are investing heavily in its development. For example, liquid renewable hydrogen is revolutionizing the aviation industry and is being explored for heavy-duty transportation, including maritime shipping.
- In addition to generating electricity, renewable hydrogen has been used to produce potable water, proving useful in space missions by providing drinking water for crews.
Advantages of renewable hydrogen
100% sustainable alternative
Renewable hydrogen reduces greenhouse gas emissions during its production. It is a sustainable option that can be implemented locally, whether at large facilities or smaller setups.
It thus functions as a local energy source. When used as an electricity producer, it will enable us to meet the increase in global energy demand in the coming years (it is expected to grow by 25 to 30%). Its use will allow us to save millions of tons of CO2 emissions.
Keep learning: Liquid hydrogen storage: learn the basics
Support for clean fuel adoption
Hydrogen combustion does not produce harmful emissions, preventing greenhouse effects and promoting clean energy solutions.
Easy to store and transport
Hydrogen is straightforward to store and versatile in its applications, from electricity generation to domestic and industrial uses. Reducing transportation costs makes it an excellent choice for heavy-duty sectors, particularly maritime transport, where its price and logistical advantages rival those of natural gas.
Significant economic support
Its potential has garnered substantial financial backing from governments. For instance, Spain’s government announced a €150 million funding initiative in February 2022 to support pioneering renewable hydrogen projects.

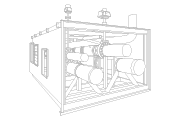
Cryospain: Specialists in renewable hydrogen infrastructure
At Cryospain, we work on pioneering projects to help companies access renewable hydrogen and advance energy decarbonization.
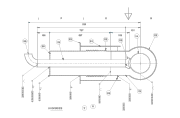
One key aspect of renewable hydrogen is its storage and transport, especially in liquid form, which requires cryogenic temperatures for preservation. Since hydrogen’s boiling point is −252.8°C at atmospheric pressure, liquid renewable hydrogen demands advanced cryogenic storage solutions.
This is where Cryospain’s expertise stands out, providing engineering solutions for the cryogenic storage of renewable H2.
Among our most notable projects is our collaboration in applying renewable hydrogen as a maritime fuel, contributing to a decarbonized sector.
Want to learn more about storage and transportation solutions for renewable hydrogen? Contact us!




 Kontaktieren Sie uns
Kontaktieren Sie uns